The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a popular technical indicator used in trading to measure the magnitude of recent price changes and assess whether a stock or asset is overbought or oversold. Traders typically use the RSI on a scale of 0 to 100, with readings above 70 indicating overbought conditions and readings below 30 indicating oversold conditions. However, advanced traders often use more complex strategies beyond these basic interpretations. Let’s dive deeper into advanced RSI strategies.
1. RSI Divergence Strategy
Divergence occurs when the price of an asset is moving in the opposite direction of the RSI. This is often a signal that a reversal is imminent.
- Bullish Divergence: When the price makes a lower low, but the RSI makes a higher low, it can indicate that the downside momentum is weakening and a bullish reversal might be near.
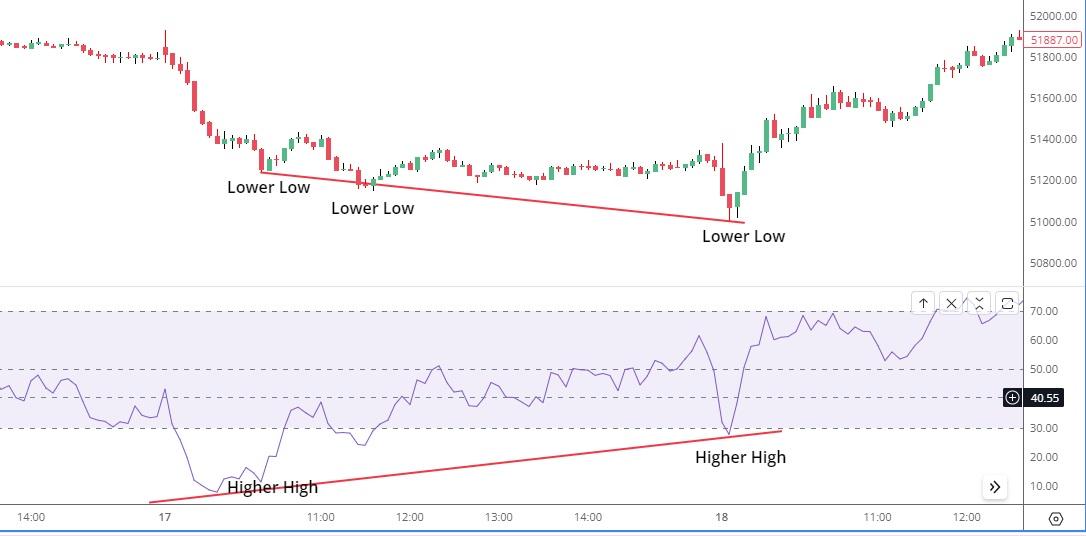
- Bearish Divergence: When the price makes a higher high, but the RSI makes a lower high, it can signal that upward momentum is weakening, potentially leading to a bearish reversal.
How to use it:
- Look for bullish divergence at the end of a downtrend and bearish divergence at the top of an uptrend.
- Combine divergence signals with other technical indicators (such as support and resistance levels) to improve accuracy.
2. RSI Trendline Strategy
The RSI chart itself can form trendlines that act similarly to those in price charts. Drawing trendlines on the RSI chart helps traders spot potential breakouts or breakdowns before they appear on the price chart.
- Bullish RSI Breakout: When the RSI breaks above a trendline, it can signal an upcoming price breakout.
- Bearish RSI Breakdown: If the RSI breaks below a trendline, it could indicate a possible price breakdown.
How to use it:
- Draw trendlines connecting the RSI peaks and valleys.
- Watch for the RSI to break its trendline before entering a position in the price chart.
3. RSI Swing Rejections
Swing rejection is a strategy where traders focus on RSI behavior rather than relying only on divergence. This method emphasizes watching for the RSI to reject a specific level and swing back in the opposite direction.
- Bullish Swing Rejection:
- RSI falls below 30 (oversold level).
- RSI crosses back above 30.
- RSI makes a pullback, but stays above 30.
- RSI breaks its previous high.
This can signal a bullish trend reversal.
- Bearish Swing Rejection:
- RSI rises above 70 (overbought level).
- RSI crosses back below 70.
- RSI makes a pullback but stays below 70.
- RSI breaks its previous low.
This indicates a potential bearish trend reversal.
4. RSI Moving Average Crossover
This strategy involves adding a moving average to the RSI line and trading when the two lines cross.
- Bullish Signal: When the RSI crosses above its moving average, it can signal that momentum is shifting upwards.
- Bearish Signal: When the RSI crosses below its moving average, it can indicate that downward momentum is increasing.
How to use it:
- Use a short-period moving average (e.g., 9-period) to track momentum shifts more quickly.
- Combine with price action analysis to confirm signals.
5. RSI Multi-Timeframe Strategy
RSI behaves differently on different timeframes. By using RSI across multiple timeframes, traders can better understand the overall market context.
- Long-Term RSI: Use a higher timeframe (e.g., daily or weekly) to analyze the broader trend.
- Short-Term RSI: Use a lower timeframe (e.g., 15-minute or hourly) for identifying entry points in line with the long-term trend.
How to use it:
- Look for overbought/oversold conditions on the long-term chart.
- Enter trades on the short-term chart in the direction of the longer-term trend.
6. RSI Failure Swings
Failure swings, a concept introduced by Welles Wilder, the creator of the RSI, occur when the RSI moves back from extreme levels without hitting them again.
- Bullish Failure Swing: When RSI moves below 30 (oversold), rebounds, and does not reach 30 again, then moves above the recent RSI high.
- Bearish Failure Swing: When RSI rises above 70 (overbought), drops, and fails to hit 70 again, then breaks below the recent RSI low.
How to use it:
- Enter long positions on bullish failure swings and short positions on bearish failure swings.
- Use failure swings in conjunction with other trend analysis to improve performance.
Important Notes for RSI Strategies
- Avoid using RSI in isolation: RSI signals become more powerful when combined with other indicators like moving averages, MACD, or trendlines.
- Understand market conditions: In strong uptrends, RSI may remain overbought for extended periods, and in downtrends, RSI may stay oversold. Adapt your strategy to the market condition.
- Adjust RSI period: Most traders use a 14-period RSI, but shorter or longer periods can give different insights. For more sensitive signals, use a shorter period like 7, and for less frequent but more accurate signals, a longer period like 21 might work better.
Visual Example of RSI Divergence Strategy:
(Image Description): In this image, we can show a price chart with RSI beneath it. The price chart illustrates a bearish divergence pattern, where the price forms higher highs, but the RSI forms lower highs. A trend reversal follows this divergence.
One advanced way to use RSI is by combining overbought and oversold conditions with trend confirmation indicators. This allows traders to filter out false signals by only acting on those that align with the broader trend.
- In an Uptrend: Look for oversold conditions (RSI below 30) to enter long positions. Avoid selling simply because RSI is overbought.
- In a Downtrend: Look for overbought conditions (RSI above 70) to enter short positions. Avoid buying just because RSI is oversold.
How to use it:
- Identify the overall trend using a trend-following indicator, such as a moving average or trendline.
- Only act on RSI signals that align with the prevailing trend (e.g., buy on oversold during an uptrend, sell on overbought during a downtrend).
8. RSI and Fibonacci Retracement
Another advanced strategy involves combining RSI with Fibonacci retracement levels. This helps traders find potential turning points in the market where price might reverse, and RSI can confirm these levels.
- Bullish Example: During a retracement in an uptrend, RSI shows oversold conditions at a key Fibonacci retracement level (e.g., 50% or 61.8%). This could signal a buying opportunity.
- Bearish Example: In a downtrend, price retraces to a key Fibonacci level and RSI reaches overbought conditions, indicating a potential short entry.
How to use it:
- Use Fibonacci retracement levels to find important support and resistance levels.
- Combine these levels with RSI overbought/oversold readings to identify possible trade entry points.
9. RSI Two-Period Strategy
This strategy is particularly useful for short-term traders who want to capture quick movements in the market. It involves using a very short RSI period (like 2-period) to catch overbought or oversold conditions for swift trades.
- For Long Entries: Wait for the 2-period RSI to drop below 10 (indicating a short-term oversold condition) and buy when it crosses back above 10.
- For Short Entries: Wait for the 2-period RSI to rise above 90 (indicating a short-term overbought condition) and sell when it drops below 90.
How to use it:
- This strategy works best in highly liquid markets with tight spreads.
- Use a very short timeframe (like 1-minute or 5-minute charts) for quick entries and exits.
10. RSI Channel Strategy
In this approach, traders plot a channel around the RSI, setting custom overbought and oversold levels based on the asset’s volatility. This can help filter out false signals in trending markets.
- Dynamic Overbought/Oversold Levels: Instead of relying strictly on 70 and 30 levels, adjust them based on the asset’s volatility or historical behavior. For example, you might use 80 for overbought and 20 for oversold in highly volatile markets.
How to use it:
- Customize your RSI channel for each asset based on its historical volatility. The higher the volatility, the wider the RSI channel should be.
- Trade the breakout of the RSI channel for trend continuation, or use channel support/resistance to find reversal points.
11. RSI Smoothing with Moving Averages
Some traders apply smoothing techniques to the RSI to reduce noise and false signals. By combining the RSI with moving averages, you can smooth the indicator and reduce the impact of erratic price movements.
- Bullish Signal: When a smoothed RSI line crosses above a moving average of RSI, it suggests that upward momentum is building.
- Bearish Signal: When the smoothed RSI line crosses below a moving average of RSI, it signals that downward pressure is increasing.
How to use it:
- Apply a short-term moving average to the RSI line, such as a 3-period or 5-period SMA.
- Enter trades when the smoothed RSI crosses above (bullish) or below (bearish) the moving average.
12. RSI Confluence with MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
The RSI and MACD are both momentum indicators, but they measure momentum in different ways. Using them together can provide more robust signals.
- Bullish Confluence: When both the RSI and MACD give bullish signals simultaneously (e.g., RSI is oversold and MACD has a bullish crossover), the likelihood of a trend reversal increases.
- Bearish Confluence: If both indicators signal bearish momentum (e.g., RSI is overbought and MACD shows a bearish crossover), a trend reversal to the downside is more likely.
How to use it:
- Look for overbought/oversold RSI readings that coincide with MACD crossovers or divergence for higher-confidence trades.
- Use confluence as confirmation of a trend change before entering trades.
Tips for Success with Advanced RSI Strategies:
- Backtest Your Strategies: Before implementing any of these advanced RSI strategies in live markets, backtest them on historical data to ensure they work in your chosen asset class and timeframe.
- Adapt to Market Conditions: RSI performs differently in trending and ranging markets. Make sure to adjust your strategy depending on whether the market is in a strong trend or trading sideways.
- Use Risk Management: Always implement proper risk management by using stop losses and position sizing to protect against unexpected market movements.
Combining the RSI with Bollinger Bands can help traders identify potential breakouts or trend reversals. Bollinger Bands measure market volatility and consist of a middle moving average band and two outer bands. When combined with RSI, this can offer a clearer picture of overbought or oversold conditions within a trending market.
- Bullish Setup: When the price touches the lower Bollinger Band and the RSI is in oversold territory (below 30), it can indicate a potential buying opportunity.
- Bearish Setup: When the price touches the upper Bollinger Band and the RSI is overbought (above 70), it could signal an opportunity to sell or short.
How to use it:
- Look for confluence between the RSI entering oversold/overbought areas and the price bouncing off Bollinger Bands.
- For more accurate signals, trade in the direction of the longer-term trend.
14. RSI and Volume Strategy
Volume is a critical component in validating RSI signals. When volume aligns with an RSI signal, it adds strength to the potential trade. High volume on an RSI signal often confirms the price direction, while low volume might indicate a false signal.
- Bullish Signal: If the RSI is oversold and volume spikes significantly, it could signal strong buying pressure and a potential upward reversal.
- Bearish Signal: When the RSI is overbought and there’s an increase in volume, it can confirm the likelihood of a downtrend or price correction.
How to use it:
- Combine RSI overbought/oversold signals with volume spikes to confirm the strength of the reversal.
- Avoid taking trades when RSI signals occur on low volume, as this could indicate weak market momentum.
15. RSI and Stochastic Oscillator Strategy
Both the RSI and the Stochastic Oscillator are momentum indicators, but they measure market conditions differently. RSI measures price momentum, while the Stochastic Oscillator compares the current price to its recent range. Using both together can help traders capture trend reversals with greater accuracy.
- Bullish Confluence: When both the RSI and Stochastic indicate oversold conditions simultaneously (RSI below 30, Stochastic below 20), it can signal a high-probability buying opportunity.
- Bearish Confluence: If both the RSI and Stochastic show overbought conditions (RSI above 70, Stochastic above 80), it may indicate a strong signal to sell or short.
How to use it:
- Wait for both indicators to align before entering a trade.
- Use these signals in combination with trendline analysis to confirm entry points.
16. RSI Median Line Crossover Strategy
This strategy focuses on the RSI crossing its mid-level (50), which indicates a shift in momentum. When the RSI moves above 50, it suggests bullish momentum, and when it drops below 50, it indicates bearish momentum. This strategy is useful for trading in trending markets.
- Bullish Signal: When RSI crosses from below 50 to above 50, it can be a signal that bullish momentum is gaining strength.
- Bearish Signal: If RSI crosses from above 50 to below 50, it may indicate that bearish momentum is taking over.
How to use it:
- Use the 50-level as a confirmation tool for ongoing trends, combining it with other indicators like moving averages to confirm direction.
- The RSI crossover can help you decide when to add to positions in a trending market or exit trades.
17. RSI and Price Action Strategy
Price action trading focuses on analyzing the price movement itself, without relying on lagging indicators. However, combining price action with the RSI can provide traders with a powerful confirmation tool to assess market conditions.
- Bullish Price Action with RSI: If the price forms a bullish pattern (like a hammer candlestick or double bottom) while the RSI shows oversold conditions, it increases the probability of a strong reversal.
- Bearish Price Action with RSI: When the price forms a bearish pattern (like a shooting star or double top) and RSI shows overbought conditions, it can strengthen the case for a trend reversal.
How to use it:
- Use candlestick patterns and chart patterns (e.g., head and shoulders, triangles) in combination with RSI to increase trade confirmation.
- RSI can help determine whether a price action pattern is likely to result in a strong reversal or a false breakout.
18. RSI and Moving Average Confluence
Moving averages are one of the most widely used indicators in trading, and combining them with RSI can give traders a clearer sense of trend direction and potential trade opportunities.
- Bullish Signal: When RSI shows oversold conditions, and the price bounces off a key moving average (like the 50-period or 200-period), it could signal a strong buying opportunity.
- Bearish Signal: If RSI is overbought and the price rejects a key moving average, it could indicate a good time to sell or short.
How to use it:
- Combine RSI signals with moving averages to increase the reliability of your trades.
- Look for moving average crossovers (such as the 50-day crossing above the 200-day) combined with RSI levels for stronger confirmation.
19. RSI Failure Patterns with Trend Analysis
RSI failure patterns, introduced by Welles Wilder, occur when the RSI fails to exceed a previous high or low. These failure swings can signal trend reversals and are often used in conjunction with trendlines and support/resistance levels.
- Bullish Failure Pattern: If RSI drops below 30, rebounds but fails to make a new low, and then breaks above a recent RSI peak, it could indicate a trend reversal.
- Bearish Failure Pattern: When RSI rises above 70, drops, and fails to make a new high, followed by a breakdown below a recent RSI low, it may signal a reversal to the downside.
How to use it:
- Look for RSI failure patterns at major support and resistance levels to increase the chances of successful trades.
- Use these patterns in trending markets to capture early signs of reversals.
Final Thoughts on RSI Strategies
Advanced RSI strategies can offer powerful insights into market momentum, trend strength, and potential reversals. However, it’s essential to remember that no strategy is foolproof. Traders should combine RSI with other technical analysis tools—such as trendlines, support and resistance, moving averages, and volume—to confirm signals. Additionally, backtesting and practicing in demo environments can help improve the success rate of these strategies in live markets.
Different asset classes, such as stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies, exhibit unique behaviors and volatility patterns. Adapting your RSI strategies based on the asset class you are trading can lead to better outcomes.
- Stocks: Stocks tend to follow trends, and RSI can effectively identify overbought or oversold conditions in strong markets. Use longer periods of RSI to smooth out the noise in volatile stocks.
- Forex: Forex markets can be more influenced by economic news and geopolitical events. Consider using a shorter RSI period (like 7 or 10) for more responsive signals and adjust the overbought/oversold levels to account for market volatility.
- Commodities: Commodities are often subject to cyclical trends. RSI can help identify both short-term and long-term overbought/oversold conditions, particularly when combined with seasonal analysis.
- Cryptocurrencies: Given their high volatility, cryptocurrencies may require shorter RSI periods (e.g., 5 or 7) to capture rapid price movements. Adjust the overbought/oversold levels based on historical volatility.
How to use it:
- Analyze the historical performance of the RSI in the specific asset class you are trading.
- Tailor your strategies to account for the unique characteristics of each asset class.
21. Combining RSI with Fundamental Analysis
While technical indicators like RSI focus on price action, combining them with fundamental analysis can lead to a more comprehensive trading approach. Understanding the underlying factors influencing price can enhance decision-making.
- Economic Indicators: In forex trading, economic indicators like GDP growth, unemployment rates, and interest rates can significantly affect currency movements. Use RSI to identify potential entry points in the context of these economic factors.
- Earnings Reports: For stocks, consider using RSI in conjunction with earnings reports and company news. A positive earnings surprise can lead to a bullish reversal even if RSI shows overbought conditions.
- Market Sentiment: Monitoring overall market sentiment through news and social media can help contextualize RSI signals. For instance, positive news may push prices higher, allowing for more extended periods of overbought conditions.
How to use it:
- Stay informed about economic and company-specific events that could impact your trades.
- Use RSI as a timing tool to enter trades aligned with fundamental catalysts.
22. Risk Management and Position Sizing
Regardless of the RSI strategies you employ, effective risk management and position sizing are crucial for long-term trading success. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Use Stop Loss Orders: Implement stop loss orders to protect against unexpected market movements. Place stop losses based on recent price action or volatility measures.
- Position Sizing: Determine your position size based on your risk tolerance. Avoid risking more than a small percentage of your trading capital (typically 1-2%) on a single trade.
- Adjust Based on Volatility: In high-volatility environments, consider reducing position sizes to manage risk more effectively. Conversely, you can increase your position size in low-volatility conditions.
How to use it:
- Develop a comprehensive risk management plan that includes position sizing, stop losses, and profit targets.
- Regularly review and adjust your risk management strategy based on market conditions.
23. Continuous Learning and Strategy Optimization
The financial markets are dynamic, and successful traders continuously learn and adapt their strategies. Here are some ways to optimize your RSI strategies:
- Backtesting: Regularly backtest your RSI strategies on historical data to assess their performance. This helps identify strengths and weaknesses and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Paper Trading: Use a demo account to practice your strategies without risking real capital. This allows you to refine your approach in real market conditions.
- Journaling: Keep a trading journal to document your trades, including the rationale behind each entry and exit. Analyze your performance regularly to identify patterns and areas for improvement.
How to use it:
- Set aside time for regular review and analysis of your trading strategies.
- Stay updated on new tools, techniques, and market trends to enhance your trading knowledge.
Understanding broader market conditions is vital for maximizing the effectiveness of RSI strategies. Market phases, such as bullish, bearish, or sideways markets, can significantly influence how RSI signals should be interpreted.
- Bull Markets: In strong bull markets, the RSI may remain in the overbought region (above 70) for extended periods. Traders should be cautious about shorting solely based on RSI overbought conditions and look for bullish confirmation signals instead.
- Bear Markets: In bearish conditions, RSI may remain in the oversold region (below 30) longer. Look for signs of trend reversal rather than automatically buying on oversold signals.
- Sideways Markets: In ranging markets, RSI can be more effective for identifying entry and exit points. Use overbought and oversold levels to capture short-term price movements.
How to use it:
- Assess the overall market trend before making trading decisions based on RSI.
- Adapt your approach based on the prevailing market condition to enhance your trade timing and execution.
25. Using RSI in Different Timeframes
The RSI can be applied across various timeframes, each serving different trading styles. Understanding how to adjust RSI settings for different timeframes can improve your trading effectiveness.
- Day Trading: For short-term trades, consider using a shorter RSI period (like 5 or 7) to capture quick price movements. This can help identify rapid overbought and oversold conditions.
- Swing Trading: For swing traders, a medium RSI period (14 or 21) works well to capture larger price swings over several days. This period balances sensitivity and reliability.
- Long-Term Investing: For long-term traders or investors, a longer RSI period (such as 30) can provide insights into major market trends and cycles. This helps in identifying entry points for longer-term positions.
How to use it:
- Choose the appropriate RSI period based on your trading style and timeframe.
- Combine signals from multiple timeframes for confirmation and enhanced decision-making.
26. Identifying Divergence
Divergence occurs when the price of an asset moves in the opposite direction of the RSI, indicating potential reversals. Recognizing divergence can enhance your trading strategies significantly.
- Bullish Divergence: This occurs when the price makes lower lows while the RSI makes higher lows. It suggests that the selling pressure is weakening, potentially leading to a reversal upward.
- Bearish Divergence: This happens when the price makes higher highs while the RSI makes lower highs, indicating that buying pressure is weakening and a downward reversal may occur.
How to use it:
- Monitor for divergence signals in conjunction with other RSI indicators to confirm potential reversal points.
- Use divergence in combination with support and resistance levels for greater accuracy.
27. Setting Alerts for RSI Signals
Setting alerts for specific RSI levels can help traders stay informed without constantly monitoring the charts. This allows you to react promptly to market conditions that meet your trading criteria.
- Overbought/Oversold Alerts: Set alerts for when RSI reaches specific overbought or oversold levels (e.g., 70 and 30) to notify you of potential trading opportunities.
- Crossing the Midline Alerts: Alerts for when the RSI crosses the 50 level can indicate potential changes in momentum, prompting you to evaluate your positions.
How to use it:
- Utilize trading platforms that offer alert features to set up notifications for RSI conditions.
- Respond quickly to alerts to take advantage of potential trading opportunities.
28. Psychology of Trading with RSI
Understanding the psychological aspects of trading is crucial when using RSI strategies. Emotions can often cloud judgment, leading to impulsive decisions that deviate from your trading plan.
- Overconfidence: Traders may become overconfident when they experience a series of winning trades based on RSI signals. This can lead to taking larger risks than intended.
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): RSI can create a sense of urgency when overbought or oversold signals appear, leading to impulsive trading decisions. Stick to your strategy and avoid chasing prices.
- Loss Aversion: Traders often fear taking losses, leading to holding onto losing positions too long, hoping for a reversal. Use stop-loss orders to mitigate this tendency.
How to use it:
- Develop a solid trading plan with predefined entry and exit rules based on your RSI strategy.
- Remain disciplined and adhere to your strategy, regardless of emotional influences.
29. Evaluating Performance and Making Adjustments
Regular evaluation of your trading performance is vital for growth. Analyze your successes and failures to identify areas for improvement in your RSI strategies.
- Track Key Metrics: Monitor win rates, average gain/loss per trade, and overall profitability. This helps you understand the effectiveness of your RSI strategies.
- Review Trade Journals: Analyze your trading journal to identify patterns in your decision-making process. Determine what worked, what didn’t, and why.
How to use it:
- Set a routine for reviewing your trading performance—daily, weekly, or monthly.
- Make adjustments to your strategies based on your findings to enhance future performance.
30. Final Words of Encouragement
Mastering advanced RSI strategies requires time, practice, and a commitment to ongoing learning. While the RSI can be a powerful tool in your trading toolkit, success comes from understanding its limitations, adapting it to various market conditions, and using it in conjunction with other indicators and analysis techniques.
As you explore and refine your RSI strategies, remember that trading is a journey. Embrace the learning process, remain patient, and stay disciplined in your approach. With dedication and continuous improvement, you can increase your confidence and effectiveness as a trader.
Conclusion
Incorporating these advanced RSI strategies into your trading can significantly enhance your ability to identify market opportunities and improve your overall trading performance. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced trader, focusing on a disciplined approach, adapting to market conditions, and maintaining a commitment to learning will lead you toward long-term trading success.
Also read: Fibonacci Trading Strategy Explained: Unlocking the Secrets of Fibonacci in Trading
